Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Materials Transactions, 64(11), p.2553 - 2559, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We attempted to calculate the hydrogen trapping energies on the incoherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates and Mg
precipitates and Mg Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg
Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg Si in the aluminum matrix.
Si in the aluminum matrix.
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
Sato, Yohei*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Miyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Terauchi, Masami*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(5), p.950 - 954, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dilute Mg-Zn-Y alloy with a mille-feuille structure (MFS) exhibits a mechanical strength comparable to Mg-Zn-Y alloy with long period stacking/ordered (LPSO) structure through kink deformation. In order to deepen understanding the thermal stability of the MFS-type Mg alloys, it is required to clarify the solute cluster structures composed of Zn and Y in solute enriched stacking faults (SESFs). In this study, electron energy-loss and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy based on scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM-EELS/EDS) were conducted to investigate the electronic structure and composition of Zn and Y in the SESFs of the MFS-Mg alloy. Zn-L2,3 spectra indicated that the valence charges of Zn in the dilute Mg alloy were different from that of the LPSO-type Mg-Zn-Y alloy. In addition, the intensity ratio of L3/L2 in Y-L2,3 spectrum of the dilute MFS-Mg alloy was larger than that of the LPSO-Mg alloy, reflecting the electron occupancies of 4d3/2 and 4d5/2 orbitals of Y atoms were different from those of the LPSO-Mg alloys. STEM-EELS analysis of the SESF composition in the dilute MFS-Mg alloy indicated that the Zn/Y ratio should be lower than that of the LPSO-Mg alloy, which was confirmed also by STEM-EDS measurements. These results indicate that the cluster structure in the SESFs of the dilute MFS-Mg alloy should be different from the ideal Zn6Y8 cluster in the LPSO-type Mg-Zn-Y alloys.
Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Egusa, Daisuke*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.813 - 816, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Materia, 62(3), p.175 - 181, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Cooper, M. W. D.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.9808_1 - 9808_11, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 66(4), p.141 - 145, 2022/04
Metal corrosion is a material deterioration phenomenon based on electrochemical reactions on an atomic scale. In this paper, various methods for acquiring physical properties on metal surfaces using first-principles calculations were described. As examples of applying first-principles calculation to metal corrosion, the effect of hydrogen adsorption on the metal surface on the potential change and the effect of cation atoms in the aqueous solution on the corrosion resistance of the metal were reported.
 -clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state character
-clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state characterOtsuka, Takaharu; Abe, Takashi*; Yoshida, Toru*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Itagaki, Naoyuki*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Vary, J. P.*; Maris, P.*; Ueno, Hideki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.2234_1 - 2234_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:95.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
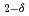 CoGa
CoGa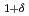 films
filmsKubota, Takahide*; Takano, Daichi*; Kota, Yohei*; Mohanty, S.*; Ito, Keita*; Matsuki, Mitsuhiro*; Hayashida, Masahiro*; Sun, M.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(4), p.044405_1 - 044405_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:59.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)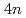 self-conjugate nuclei in
self-conjugate nuclei in  no-core Monte Carlo shell model calculations with nonlocal
no-core Monte Carlo shell model calculations with nonlocal 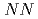 interactions
interactionsAbe, Takashi*; Maris, P.*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Vary, J. P.*
Physical Review C, 104(5), p.054315_1 - 054315_22, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:76.16(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Nagai, Yuki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 155(3), p.034106_1 - 034106_9, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.89(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Tsuru, Tomohito
AIP Advances (Internet), 11(6), p.065012_1 - 065012_7, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.85(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In the current study, we analyzed the self-interstitial atoms (SIAs) in BCC molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W) in comparison with other BCC transition metals utilizing first-principles method; particularly, we focused on uncommon dumbbells, whose direction are inclined from  111
111 toward
toward  110
110 on the {110} plane. Such a direction is not stable neither in the group 5 BCC metals (i.e., vanadium, niobium, and tantalum) nor in
on the {110} plane. Such a direction is not stable neither in the group 5 BCC metals (i.e., vanadium, niobium, and tantalum) nor in  -iron. Our first-principles relaxation simulations indicated that inclined dumbbells were more energetically-favored than common
-iron. Our first-principles relaxation simulations indicated that inclined dumbbells were more energetically-favored than common  111
111 dumbbells in Mo, while this is not necessarily the case for W. However, under a certain degree of lattice strain, such as shear or expansive strain, could make inclined dumbbells more favored also in W, suggesting that the lattice strain can substantially influence the migration barrier of SIAs in these metals because inclined dumbbells generally have a larger migration barrier than
dumbbells in Mo, while this is not necessarily the case for W. However, under a certain degree of lattice strain, such as shear or expansive strain, could make inclined dumbbells more favored also in W, suggesting that the lattice strain can substantially influence the migration barrier of SIAs in these metals because inclined dumbbells generally have a larger migration barrier than  111
111 dumbbells.
dumbbells.
Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Computational Materials Science, 188, p.110173_1 - 110173_14, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 molecule adsorption on polar and
molecule adsorption on polar and  -plane surfaces of GaN
-plane surfaces of GaNSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Asai, Yuya*; Tamura, Ryo*; Uedono, Akira*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(46), p.25282 - 25290, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.15(Chemistry, Physical)The initial oxidation of different GaN surfaces [the polar Ga-face (+c) and N-face (-c) and the nonpolar (10 0) (
0) ( )plane] under O
)plane] under O molecular beam irradiation was studied by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT molecular dynamics calculation. The results predict that triplet O
molecular beam irradiation was studied by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT molecular dynamics calculation. The results predict that triplet O either dissociates or chemisorbs at the bridge position on the +c-surface, while on N-terminated -c-surface the O
either dissociates or chemisorbs at the bridge position on the +c-surface, while on N-terminated -c-surface the O 2 molecule only undergoes dissociative chemisorption. On the
2 molecule only undergoes dissociative chemisorption. On the  -GaN surface, although the dissociation of O
-GaN surface, although the dissociation of O is dominant, the bond length and angle were found to fluctuate from those of O
is dominant, the bond length and angle were found to fluctuate from those of O molecules adsorbed on the polar surfaces. The computational model including both the surface spin and polarity of GaN is useful for understanding the interface between GaN and oxide layers in metal-oxide electronic.
molecules adsorbed on the polar surfaces. The computational model including both the surface spin and polarity of GaN is useful for understanding the interface between GaN and oxide layers in metal-oxide electronic.
 U
U O
O
Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kitagaki, Toru; Hoshino, Takanori; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.915 - 921, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)To elucidate the mechanical properties of fuel debris inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, we use first-principles calculations to evaluate mechanical properties of cubic Zr U
U O
O , which is a main component of the fuel debris. We focus on the dependence of mechanical properties on the fraction x of zirconium, compare our results with recent experiment of simulated debris, in which dependences of elastic moduli and fracture toughness on the ZrO
, which is a main component of the fuel debris. We focus on the dependence of mechanical properties on the fraction x of zirconium, compare our results with recent experiment of simulated debris, in which dependences of elastic moduli and fracture toughness on the ZrO content showed deviation from a simple linear relation. We show that elastic moduli drop at around x=0.25 and increase again for larger values of x, as has been observed in experiments. The reason of the drop is a softening owing to disordered atomistic structures induced by the solute zirconium atoms. We also find that stress-strain curves for the x=0.125 case show marked hysteresis owing to the existence of many meta-stable states. We show that this hysteresis leads to slightly increased fracture toughness, but it is not enough to account for the significant increase of fracture toughness observed in experiments.
content showed deviation from a simple linear relation. We show that elastic moduli drop at around x=0.25 and increase again for larger values of x, as has been observed in experiments. The reason of the drop is a softening owing to disordered atomistic structures induced by the solute zirconium atoms. We also find that stress-strain curves for the x=0.125 case show marked hysteresis owing to the existence of many meta-stable states. We show that this hysteresis leads to slightly increased fracture toughness, but it is not enough to account for the significant increase of fracture toughness observed in experiments.
 Cs solid-state NMR and density functional theory calculations
Cs solid-state NMR and density functional theory calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Okamoto, Takuya*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Gu gan, R.*; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
gan, R.*; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 122(48), p.9326 - 9337, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:60.51(Chemistry, Physical)The structures of Cs adsorption on montmorillonite were investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The NMR spectra of Cs adsorbed on montmorillonite samples were measured under different Cs contents and relative humidity levels. NMR parameters were evaluated by the first principle calculations in order to identify the relationship between adsorbed Cs structures and NMR parameters. The comparisons between experimental and theoretical NMR spectra revealed that Cs is preferentially adsorbed at sites near Al for low Cs substituted montmorillonites, and that non-hydrated Cs present in partially Cs substituted samples, even after being hydrated under high relative humidity.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Keikinzoku, 68(11), p.596 - 602, 2018/11
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) is considered as one cause of stress corrosion cracking. HE is a serious problem in the development of high strength aluminum alloy as with steels. For understanding HE, it is inevitable to know hydrogen trapping states in the alloys and it can be identified using thermal desorption spectrometry of H. In this study, we numerically simulated thermal desorption spectra of hydrogen in aluminum for a cylindrical and a plate specimens and interpreted the desorption peaks included in them on the basis of the trap site concentration and the trap energy. As a result, we found that the peak at the lowest-temperature side can result from grain boundaries and confirmed that the reported interpretation for other peaks is reasonable. We also obtained the result showing the possibility that the trap site concentration of defects changes during heating the specimens. This result may give a suggestion for the interpretation of temperature desorption spectra of steels.
Okumura, Masahiko; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Lammers, L. N.*; Ikeda, Takashi*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 189, p.135 - 145, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:87.2(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
 3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 26(6), p.065005_1 - 065005_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation-induced grain boundary phosphorus segregation is an important factor for estimating the embrittlement of nuclear reactor pressure vessel steels, but the physical process of phosphorus migration to grain boundaries is still unclear. We numerically studied phosphorus migration toward  3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary in  -iron using molecular dynamics. We found that, in the vicinity of the grain boundary within
-iron using molecular dynamics. We found that, in the vicinity of the grain boundary within  1 nm distance, an iron-phosphorus mixed dumbbell and an octahedral interstitial phosphorus atom push a self-interstitial atom into the grain boundary, and the phosphorus atom becomes a substitutional atom. A phosphorus vacancy complex in the region also becomes dissociated, and the vacancy is absorbed in the grain boundary without dragging phosphorus. The results claim that a novel view of the segregation process is required.
1 nm distance, an iron-phosphorus mixed dumbbell and an octahedral interstitial phosphorus atom push a self-interstitial atom into the grain boundary, and the phosphorus atom becomes a substitutional atom. A phosphorus vacancy complex in the region also becomes dissociated, and the vacancy is absorbed in the grain boundary without dragging phosphorus. The results claim that a novel view of the segregation process is required.